This article has been updated to show that the botnet is not infecting other nodes on Lightning but operating as a traditional botnet would—instead using Lightning to communicate with its servers in one part of the botnet.
Bitcoin’s Lightning is a faster, cheaper way of sending bitcoin around. But it might be a much more effective way of sending messages to control a botnet too.
Researchers at Florida International University published the paper on December 24, outlining why Lightning’s perks of anonymity and a lack of censorship make it attractive to botmasters—the criminal masterminds behind botnet attacks. They argued that these benefits provide many advantages for remotely controlling malicious software. And, case in point, they even built a proof of concept themselves, LNBot, a covert hybrid botnet.
Ahmet Kurt, co-author of the paper and researcher at the Advanced Wireless and Security Lab, told Decrypt, “We think it is extremely hard to shut it down. We listed some potential countermeasures but the community can find some other possible countermeasures to stop such attacks.”
A botnet is created when a hacker installs malware—infectious computer programs—onto a large number of computers and uses it to take control of them. The bot master can then use these computers he or she controls for nefarious reasons. The botmaster uses what’s known as a command and control (C&C) servers to control the computers without giving away his or her identity.
According to the research paper, the botmaster would infect computers with malware, and use them to spin up a Lightning node. These then become the C&C servers that it uses to run multiple mini botnets. The Lightning network is then used for communication with the servers, telling them how to run their mini botnets. The point being, if the C&C servers get discovered, it doesn't point back to the original botmaster.
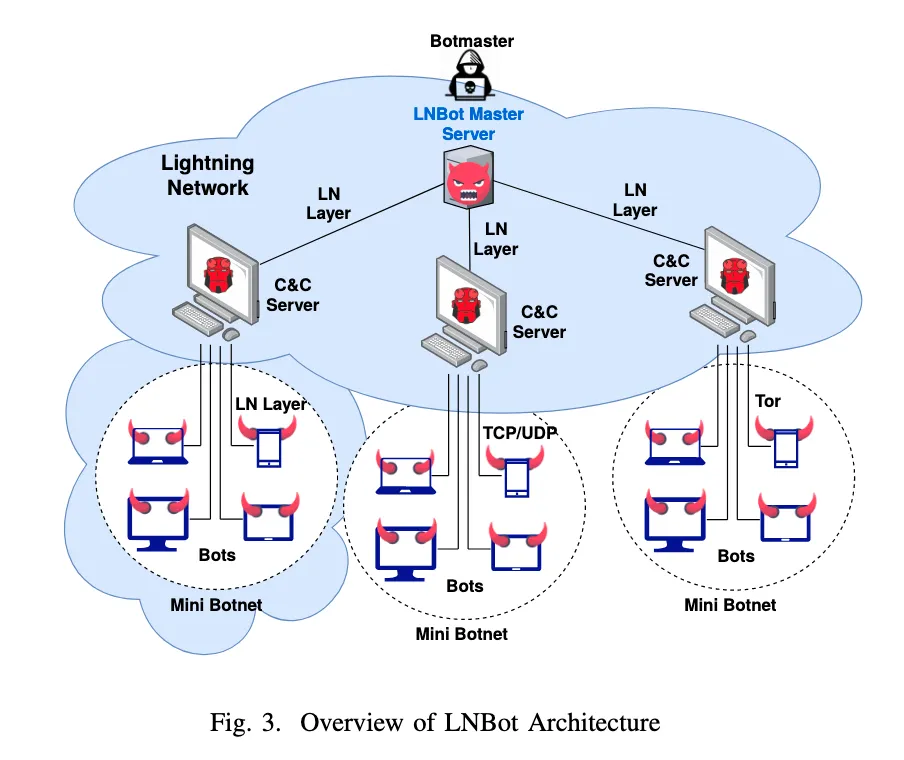
However, according to the paper, hackers have found it hard to maintain centralized C&C servers without getting caught. As a result they have tried more covert channels, such as social media networks. But these are undermined by users not always being logged in. Instead, hackers have tried using peer-to-peer technologies, such as Bitcoin. But with Bitcoin, all commands are publicly available, which makes it hard for the hacker to remain undetected. So none of these will quite do.
Rather, the answer to Bitcoin’s scaling problem, Lightning, might well be the botmasters’ solution.
Secretive communications
Lightning is a second-layer scaling solution built on the Bitcoin blockchain. It’s designed to handle millions more transactions at a much lower cost. It works a bit like a bar tab, you can make payments with anyone and at any point either party can close the tab, and settle it on the Bitcoin blockchain.
“In this paper, we advocate [Lightning] as an ideal C&C infrastructure for botnets with all the aforementioned features (i.e.,faster transactions, decreased costs). Specifically, [Lightning] offers bot masters numerous advantages over existing techniques,” said the researchers.
Lightning has a few benefits. First, transactions have a much greater degree of anonymity and transactions are not publically available on a ledger—unlike Bitcoin. However, this means that the botmaster can communicate more secretly with the C&C server.
Second, knowing where one C&C server is doesn’t reveal the location of any other C&C servers—enabling the botmaster to have multiple ways of controlling the botnet. Although there is a silver lining. “Even though taking down the C&C servers neither reveals the botmaster nor stops the botnet as a whole, it shuts down a part of the botnet resulting in less damage to victims,” the paper stated.
Third, communication from the C&C server cannot be censored, according to the researchers. Since Lightning is a peer-to-peer network, there is no central authority dictating what messages can or can’t be passed around. While there are watchtowers for resolving disputes, these don’t have the power to censor messages.
According to the paper, the cost of running 100 C&C servers would be 0.06 bitcoin, worth $440 at today’s bitcoin price of $7,360. It added, “This is a one time non-recurring investment cost of forming LNBot with 100 C&C servers which is a very small amount considering the fact that each C&C server can control tens of thousands of bots.”
The main worry is that these attacks could be performed with the current version of Lightning and there are few steps to prevent them. The proof of concept the researchers built, with 100 live C&C servers, is running on the network today. They didn’t need to modify the Lightning network at all to create it. And, the paper stated, Lightning developers are working on adding a feature that would make botnets even harder to destroy.
Kurt said, “The aim of this research is to make security researchers and [Lightning] developers think about how this can be stopped.”

